This article may contain affiliate links. For details, visit our Affiliate Disclosure page.
Introduction
The placenta is a vital organ that develops during pregnancy to provide nutrients and oxygen to the growing fetus. It plays a crucial role in supporting the baby’s growth and development in the womb. The weight of the placenta varies from woman to woman and can also be affected by various factors such as gestational age, maternal health, and fetal health. In this blog post, we will explore the weight of the placenta and the factors that can influence it.
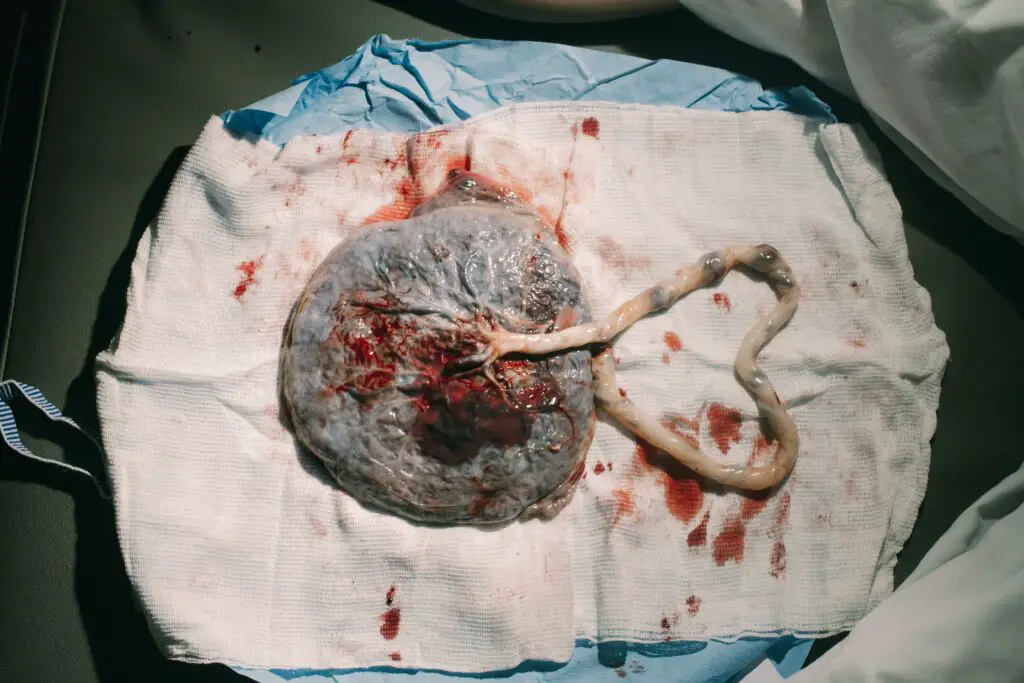
The Placenta’s Weight at Birth
The weight of the placenta at birth is a crucial indicator of fetal growth and development. It is also an essential factor in determining whether the delivery was successful or not. On average, the weight of a full-term placenta ranges from 500 to 700 grams. However, it is essential to note that the weight can vary depending on several factors, such as maternal age, parity, and gestational age.
Maternal Age and Placental Weight
Maternal age can play a role in determining the weight of the placenta. Studies have shown that older mothers tend to have smaller placentas than younger mothers. This could be due to age-related changes in the maternal body, such as decreased blood flow to the placenta, which could affect its growth and development. However, it is essential to note that the impact of maternal age on placental weight is not significant and varies from woman to woman.
Parity and Placental Weight
Parity, or the number of pregnancies a woman has had, can also affect the weight of the placenta. Studies have shown that women who have had multiple pregnancies tend to have smaller placentas than women who are pregnant for the first time. This could be due to changes in the maternal body that occur after multiple pregnancies, such as changes in the size and shape of the uterus. However, it is important to note that the impact of parity on placental weight is not significant and varies from woman to woman.
Gestational Age and Placental Weight
Gestational age, or the number of weeks a woman is pregnant, is one of the most significant factors that can affect the weight of the placenta. Studies have shown that as the gestational age increases, the weight of the placenta also increases. At 20 weeks of gestation, the placenta weighs about 150 grams, while at full term, it can weigh up to 700 grams. This increase in weight is due to the growth and development of the fetus, which requires more nutrients and oxygen as it grows.
Fetal Health and Placental Weight
The health of the fetus can also impact the weight of the placenta. Studies have shown that fetuses that are small for their gestational age tend to have smaller placentas than fetuses that are appropriately sized. This could be due to the placenta’s reduced ability to transport nutrients and oxygen to the growing fetus, which could affect its growth and development. However, it is important to note that the impact of fetal health on placental weight is not significant and varies from woman to woman.
Maternal Health and Placental Weight
Maternal health can also affect the weight of the placenta. Studies have shown that women with certain medical conditions, such as hypertension, diabetes, and preeclampsia, tend to have smaller placentas than women without these conditions. This could be due to the placenta’s reduced ability to transport nutrients and oxygen to the growing fetus, which could affect its growth and development. However, it is important to note that the impact of maternal health on placental weight is not significant and varies from woman to woman.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the weight of the placenta can vary from woman to woman and can be affected by several factors, such as maternal age, parity, gestational age, fetal health, and maternal health. While these factors can impact the weight of the placenta, it is important to note that the impact is not significant and can vary from woman to woman. Monitoring the weight of the placenta during pregnancy can provide important information about fetal growth and development and can help healthcare providers determine whether further intervention is necessary.
Overall, the weight of the placenta is an important aspect of pregnancy and childbirth that can impact the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. Understanding the factors that can influence the weight of the placenta can help women and healthcare providers make informed decisions about their pregnancy and childbirth care.
